Mad About Marble
 Karin Kirk
Karin Kirk
usenaturalstone.com
Oculus photo © Karin Kirk
 |
|
Above: Marble quarry in Carrara, Italy, a stone that’s been quarried for over 2,000 years. |
 |
|
Above: Yule marble, as featured on the exterior of the Lincoln Memorial. |
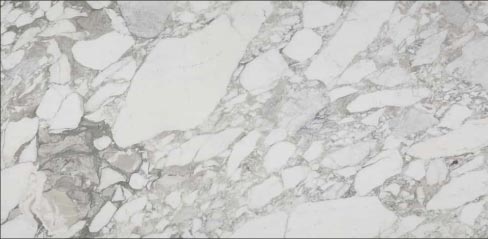 |
|
Above: Arabescato marble. |
 |
|
Above: Veria Green marble . |
 |
|
Above: The Oculus, a calming expanse of soaring white marble ribs, is part of the 9/11 site, located next to the footprint of the fallen towers. |
From the shimmering aura of the Taj Mahal, to the humble floor of a public bathroom, marble is one of the world’s most revered and useful natural materials. Marble is Michelangelo’s David, the Washington Monument, and the Duomo of Florence. It is also the primary ingredient in Tums antacid.
Tune into any kitchen design message board and you’ll encounter a sharp divide over the utility of marble. Some people wouldn’t dream of designing a kitchen without marble. Others decry that choice, citing marble’s imperfections and fragility. Many are caught somewhere in the middle: in love with marble’s irresistible appeal, but uncertain if it’s the right choice for their circumstance. In an attempt to create the “perfect” material, legions of synthetic quartz products claim to look “just like marble,” but marble enthusiasts aren’t swayed. Few stones can match the warm glow, the softly flowing colors, the timelessness, and the authenticity of marble. There’s good reason this stone has been used for over 5,000 years.
A Seabed, Transformed
Marble is a metamorphic rock; it once was a different kind of rock, and was then transformed by a change of circumstance. Before marble becomes marble, it is first limestone, which forms on the shores and floors of tropical seas. Limestone is an accumulation of shells, shelly fragments, microscopically tiny shells, and dissolved shells. Depending on the conditions at a particular beach or sea, limestone’s shelly sediment may be punctuated with occasional layers of clay or lenses of sand. But by and large, limestone is an assortment of shell-remnants, which are made of the mineral calcite.
The tropical shoals that give rise to limestone do not stay peaceful indefinitely. Oceans are basically geologic conveyor belts. The ocean floor slowly spreads apart from the center and slips underneath continents at the edges, gradually rearranging the map of the world.
When a limestone seabed gets dragged down into the Earth’s crust, the additional heat transforms the calcite grains and fuses them together tightly. The dynamic action of rock layers as they become buried, twisted, and shoved around causes the original flat-lying layers to bend, buckle, and swirl together. A rock in this heated state doesn’t melt. It’s simply warm and flexible, much like a chocolate bar left in your pocket. This process of heating and warping is responsible for marble’s trademark aesthetic of gracefully flowing bands of color. The grey swirls in marble are simply clay layers that got folded, smeared, and re-folded into the marble like a ribbon of chocolate infused throughout fudge ripple ice cream.
Patterns and Colorways Give Marble Versatility and Character
Part of what makes natural stone so appealing is the huge range of colors and variations expressed in solid rock. On one hand, these patterns tug on our heartstrings and offer aesthetic possibilities. On the other hand, each of these variations has its root in some sort of geologic process.
Most marble is white. The classic, white marble is pure calcite, without intervening minerals to lend it color. Yule and Thassos marbles are well-known examples of pristine white marbles.
But marble can take on a delightful range of hues and textures. Pink marble is tinted by iron oxide, as is golden marble. Green marble and deep red marble contain serpentine, rich in magnesium. Fossil-rich limestone becomes graphite-infused marble, as the carbon in fish, algae, or seaweed reverts back to the elemental carbon in graphite when the rock is heated. Graphite-rich marble is steely grey with a metallic glimmer.
A marble breccia is formed when the stone fractures underground, which can happen if a stone lives in a fault zone. Mineral-laden groundwater comes to the rescue, filling in the voids and patching the fragments back into a solid mass, while creating a spectacular pattern at the same time. Arabescato is a beautiful example of a marble breccia.
It’s Important to Understand the Properties of Marble
The mineral content of marble is the same as the limestone it came from, and both of these stones are made of calcite, AKA calcium carbonate, AKA CaCO3. Calcite is one of the more common minerals on Earth’s surface; in addition to limestone and marble, calcite is the primary ingredient in travertine and onyx.
Calcite has a few properties that you should know about before you fall head over heels in love with a stunning marble slab. Calcite is 3 on Mohs hardness scale, which means it will get scratched by knife blades, ceramics, and a cast iron skillet accidentally slid across the kitchen island.
Calcite is also chemically reactive with common acids, like lemonade, wine, and Coke. When acidic liquids land on a marble slab, a tiny amount of the stone is dissolved, or “etched.” This doesn’t affect the integrity of the stone, but it does leave a slight change in the color and/or luster of the stone. On a polished stone, an etch looks like an unpolished area. Etches can be polished out, or they can be left alone and considered part of the natural patina that marble will acquire over time.
Marble is ground up into antacid tablets because calcite neutralizes acid, which makes your stomach feel better. That also explains why acid makes a mark on marble. The marble reacts with the acid, neutralizing the acid, but damaging your countertop in the meantime. Ironically, when your teenager dribbles pickle juice on a brand new countertop, you may find yourself reaching for the antacid, triggering the same chemical reaction both on the countertop and in your digestive tract.
The last piece of potentially bad news is that marble can form “star cracks” if a heavy, hard object falls on it. Star cracks look like small, light-colored areas where the impact occurred.
This is usually an aesthetic issue, not a structural one, but if an impact occurs at the edge of the stone, it can chip or flake.
One thing you needn’t worry about with most marbles is staining. The metamorphism that bakes the stone also knits the minerals together tightly. Porosity for marble is similar for that of granite. That said, the porosity of all stones varies, so check the stone specs and do your own tests with a sample of stone. Marbles are typically sealed to reduce the likelihood of staining. Alas, sealing does not make marble any less prone to etching, I’m sorry to say.
Now you can see why some people love marble while others think that marble-lovers are crazy. To some, the nicks and etches on a marble surface add character and mark the passage of time in a busy household. To others, each blemish resonates as a personal loss. Which way do you see it? This is an important question to consider before you head to the slab yard.
 |
|
The Rose and Cedar varieties of Tennessee marble are the happy result just the right amount of iron oxide. |
Marble with Magnesium = Dolomite
Dolomitic marble is a close relative of regular marble. Standard marble is made of calcite (CaCO3), and dolomitic marble has a little magnesium in the mix (CaMgCO3). There is not a huge difference between the two variations, except that dolomitic marble is a little bit slower to etch. You’ll have a moment to wipe up a spill before the chemical reaction takes place.
Marble with Quartz = Confusing
While marble is primarily made of calcite, it’s possible for the original limestone to have occasional layers of sand or chert (chert is a marine rock made of pure silica). These interlopers turn into areas of quartz as marble undergoes metamorphism. The end result is a stone that is mostly calcite with some quartz. This combination of ingredients has kicked off industry-wide confusion, because calcite and quartz have distinctly different properties but they look alike.
Unfortunately, marble that contains minor amounts of quartz is sometimes labeled “soft quartzite,” which is both an oxymoron and a misnomer. There is no such thing as soft quartzite, and that term should be avoided by dealers, designers, and customers alike. Marble that contains small areas of quartz is still marble and should just be called marble. Super White is one well-known example of a mislabeled stone. Super White is a dolomitic marble with occasional bits of quartz. Super White is neither quartzite nor “soft quartzite.” It’s marble, and a gorgeous one at that. (You can learn more about the quartzite/marble labeling problem in The Definitive Guide to Quartzite.)
Limestone is Sometimes Classified as Marble
The term “marble” is often applied broadly rather than literally. Polished limestone is sometimes called marble. While there’s not a huge difference between the two, marble is much more dense and therefore is resistant to staining. If a slab has fossils, shell fragments, or has open pockets within the stone, it’s limestone.
Many stones classified as black marble are actually black limestones. This is particularly true for dark colored stones with stark white veins, like China Black, Dynasty Brown, or Nero Portoro. Because marble has origins as a fluid, heated rock, it’s stripes and veins are usually soft, flowing, and curved rather than angular.
Many Ways to Bring Marble into Our Lives
Marble remains a popular choice for countertops, backsplashes, bathrooms, tabletops, flooring, and cladding. Marble’s versatility makes it at home in an ancient Greek sculpture, in a lavish hotel lobby, or on a hardworking kitchen island. Marble also finds its way into our lives as household objects like cheese boards, rolling pins, vases, and lamps.
Despite the emergence of marble lookalikes, there’s nothing quite like the real thing. Real marble has qualities that cannot be replicated in a lab. I recently visited the 9/11 Memorial, a sobering space of monument, museum, and reflection. Next to the footprint of the fallen towers, rises the one part of the site that inspires optimism. Called the Oculus, it’s part transit center, part shopping mall, and its soaring white ribs beckon investigation.
Visitors who step inside are rewarded with a vast, cathedral-like space, covered in pure white marble. The combination of natural light, natural stone, and creative architecture transform the somber mood into a hopeful one. Wandering around the expansive structure, I finally put my finger on my favorite quality of real marble. Light penetrates into the white stone, then radiates back out in heavenly luminosity, filling the room with a warm, soft glow. Leave it to a stone like marble to completely alter the mood of a building. Marble has been a metaphor for worship, reverence, and beauty for millennia. Its ability to do that is all the more appreciated today.
To learn more, you can visit these websites:
The Many Uses of Marble, from Geology.com:
geology.com/rocks/uses-of-marble/
Different varieties of marble from Carrara:
www.litosonline.com/en/article/2017-sep-13/different-varieties-marble-carrara
More than 150 commercial varieties of marble come from the Carrara area in central Italy. This article describes many different marbles, such as Calacata, Statuary, and more.
Read more about the history of Carrara marble in Stories in Stone: Travels Through Urban Geology, by David B. Williams.
www.amazon.com/Stories-Stone-Travels-Through-Geology/dp/0802716229
Karin Kirk is a geologist and science educator with over 20 years of experience. She has taught college level geology, online courses and organized field trips. She currently works as a freelance science writer and education consultant. She brings with her a different perspective to the stone industry. Karin was an education program presenter at TISE 2018 and a regular contributor to usenaturalstone.com and the Slippery Rock Gazette.